Color
- Information conveyed only in color is not available to people who do not perceive color
- Whenever color conveys information, make sure that other parts of the page convey the same information
- This applies to link color also. Provide some formatting as well as a focus indicator, in addition to color, to differentiate links from text.
Color Coding Examples
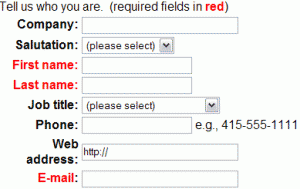
Here is an example of a common mistake; an actual customer survey modified from one on a major commercial site indicates required fields in red.
Cascading Style Sheets
- CSS is a standard layout language for the Web. CSS controls colors, typography, and the size and placement of elements and images.
- CSS,together with other web standards such as XHTML, helps separate style from content, making the Web more accessible.
- A document needs to be understandable with its style sheet turned off. Style sheets are an asset to accessibility but they are ignored by assistive technology so it is important not to convey information with style sheets. This includes images that are in style sheets. CSS images should not convey information as the alt attribute of a CSS image is not accessible by a screenreader.
Class Example
Class Example (Before, Problems, After)
WCAG 2.0 Guideline
1.4.1 Use of Color: Color is not used as the only visual means of conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response, or distinguishing a visual element.
Guideline 1.3 Create content that can be presented in different ways (for example simpler layout ) without losing information or structure.
1.3.1 Information, structure, and relationships conveyed through presentation can be programmatically determined or are available in text.
Suggested Tools to check color on a page
- IE Web Accessibility Toolbar: Use any of the tools under Color to check for contrast and color blindness usability. There are also Simulations under Tools.
- Developer’s Toolbar for Firefox: Use Tools -> Validate Section 508. This will produce a Cynthia Says report which will display which WCAG guidelines the page passed or failed. Section C. checks color and contrast.
- Use Juicy Studio’s Accessibilty plug-in for Firefox to check contrast. Go to Tools->Juicy Studio Accessibility->Color Contrast Analyzer->All Tests
Suggested Tools to check CSS
- IE Web Accessibility Toolbar:
- Validate CSS through the Check -> W3C CSS Validator
- Use the CSS menu to disable CSS on a page to make sure no information is conveyed only via CSS. Does the layout of the page still make sense with the style sheet turned off? Do items appear in the correct order?
- You can also view the associated style sheet through the CSS menu tools.
- Developer’s Toolbar for Firefox:
- Turn CSS off on a page to make sure no information is conveyed only via CSS. Disable CSS through the CSS -> Disable Styles menu item. Does the layout of the page still make sense with the style sheet turned off? Do items appear in the correct order?
- The CSS menu allows you to view the style sheet and to edit the style sheet.
- JAWS ignores style sheets so listen to the page to make sure no information is conveyed only via style sheet.