Inspired by this Friday’s presentation “Killing the Course Pack: New Methods for Providing Access to Course Readings” co-sponsored by The Center for Teaching Excellence, Instructional Technology and the Munday Library, we wanted to share some information to assist you in integrating digital supplemental course material (and course reserves) into your Canvas or Blackboard course. Photo Credit: Mariusz Kluzniak’s Lincoln’s Inn Library. Continue reading
Inspired by this Friday’s presentation “Killing the Course Pack: New Methods for Providing Access to Course Readings” co-sponsored by The Center for Teaching Excellence, Instructional Technology and the Munday Library, we wanted to share some information to assist you in integrating digital supplemental course material (and course reserves) into your Canvas or Blackboard course. Photo Credit: Mariusz Kluzniak’s Lincoln’s Inn Library. Continue reading
Tag Archives: reading
Collaborative Student Assignments Outside the Classroom
On Wednesday, February 12 at noon Instructional Technology hosted a tech snack on collaborative student assignments outside the classroom featuring Kendall Kelly, Assistant Professor of English, Writing, and Rhetoric. Dr. Kelly led a discussion that focused on these questions:
- How can we get students to interact and collaborate outside of class meetings?
- What kinds of online assignments engage students and enhance in-class learning?
 Dr. Kelly began by describing how she gets her students to collaborate online using blogs, wikis, and group spaces in Blackboard and shared a handout, “Tips for Using Blogs to Improve Student Outcomes.” These tips underline the importance of structuring the use of blogging assignments so that there are clear expectations for students and that they are rewarded for their effort. Blackboard allows Dr. Kelly to give private feedback and easily track student blogs and responses, so that this assignment does not impose an inordinate amount of work on the instructor. She says she is able to read 20 student blogs in about 30 minutes before class starts. Dr. Kelly motivates students by noting good blogs in front of the class.
Dr. Kelly began by describing how she gets her students to collaborate online using blogs, wikis, and group spaces in Blackboard and shared a handout, “Tips for Using Blogs to Improve Student Outcomes.” These tips underline the importance of structuring the use of blogging assignments so that there are clear expectations for students and that they are rewarded for their effort. Blackboard allows Dr. Kelly to give private feedback and easily track student blogs and responses, so that this assignment does not impose an inordinate amount of work on the instructor. She says she is able to read 20 student blogs in about 30 minutes before class starts. Dr. Kelly motivates students by noting good blogs in front of the class.
Dr. Kelly uses this blogging assignment to help students read challenging theoretical texts for her freshman level course on technical communication. Her writing prompts guide their reading, and, by reviewing the blogs before class, she can see what students are thinking and where they aren’t understanding the text. These insights in turn lead to a richer in-class discussion.
Blogs offer an alternative to discussion boards, which are a common and long-established mainstay of online learning. In contrast to the discussion board, blogs seem to inspire greater investment from students. They are more like mini-papers than the conversational interchange of the discussion board, and by being identified with one particular student, blogs allow for more development of a student’s voice. The focus is on the student rather than the topic, as it might be in a discussion board. In Dr. Kelly’s class, students compete to be recognized for their unique perspective in class. For example, a recent class has been vying to see who can come up with the best food analogy to explain the reading.
By using the Blackboard tool for blogs rather than a public blog, Dr. Kelly offers a safe space for student discussion while still applying the pressure of a public class audience. When asked about whether students resisted sharing their works with others, Dr. Kelly pointed out that collaborating with other students is a listed course objective on the syllabus, so students begin the course with this clear expectation. Overall, blogs allow Dr. Kelly’s students to improve their reading and writing outside of class in such a way that it raises the level of in class interaction. This instructional design is a good example of effectively linking in- and out-of-class work in a hybrid or blended learning format.
Tips for Using Blogs to Improve Student Outcomes
 Kendall Kelly, Assistant Professor of English, Writing, and Rhetoric, is our guest blogger for this post:
Kendall Kelly, Assistant Professor of English, Writing, and Rhetoric, is our guest blogger for this post:
Student blogging can create valuable learning opportunities. Blogs can provide students the chance to work on particular skills like writing, audience analysis, or critical thinking, or engage a text or project in an asynchronous, low-stakes manner. They give students a medium to engage classmates and allow the instructor to informally evaluate student comprehension before class begins. However, to facilitate student learning, instructors need to use blogs properly. Below I’ve listed some tips to maximize student learning.
- Write a prompt for each blog.
- Set a due date that gives students time to respond to one another’s blogs.
- Require students to respond to one another’s blogs.
- Set quality and quantity guidelines i.e. two paragraphs that analyze the salient point with evidence from the text.
- Grade every blog, every time. (I usually assign a point value to each blog and student response and just add them up as I go. And I give extra credit to good blogs. )
- Integrate the information from the blogs into your lectures. (Give a student a shout out for a good blog or even invite him or her to start class discussion.)
- Blogs are iterative and essentially collaborative (i.e. everyone’s reading everyone else’s blog), so one or two good bloggers can raise the bar for the class, and one or two bad bloggers can drag the class down.
- Use Blackboard for student blogs if possible.
- Blackboard allows you to give student grades. They see their grade go up with each blog which encourages them to write the next blog.
- You also have the opportunity to give students private feedback on Blackboard, so if their blogs aren’t quite up to snuff, you can let them know. Blogs are an iterative process, so if they don’t initially do well, they have the opportunity to improve.
- Blackboard will count blogs and comments for you.
- Blackboard will keep track of the grade and just put it in the grade sheet, if you set it up properly.
- And the blogs will only be available to the class which creates a safe place to write and keeps crazy outsiders from making inappropriate comments or using student information for nefarious purposes.
- Blackboard won’t allow students to post video (or at least it hasn’t in the past) or audio files so it may not work for every situation. SEUfolios will allow multi-modal media and let students manipulate the format, so it might work for those assignments.
Note: WordPress Blogs are also available to St. Edward’s University, faculty, students, and staff through http://sites.stedwards.edu/blogs/ These sites can be set up as individual blogs or a group of blogs can be set up for a class. Contact Instructional Technology for more information.
References: Image available from Wikimedia Commons, http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blog_(1).jpg
Apps for the Commuter
Last week, Profhacker’s Open Thread Wednesday asked about our favorite mobile apps. The text of my response is below, with the addition of links:
I have to give a shout out not to an app but to some built in functionality in iPads and iPhones. My commute can be up to an hour, and since public transportation is not an option that means all driving and no reading.
I find VoiceOver–one of the accessibility features on the iPad and iPhone–to be invaluable. Here’s how I include it in my workflow. During breakfast, I read RSS feeds using Mr. Reader on my iPad. (I love this app because I can send articles to Instapaper, Diigo, twitter, etc.). I send the articles I want to read later to Instapaper and make sure they download before I leave the house. (I only have wireless on my iPad, so no downloads on the road.) In the garage, I open Instapaper and ask Siri to turn on VoiceOver. Then I start my iPad reading and listen to the morning’s news while I drive. When I arrive on campus, Siri is once again working on the campus wireless network, so I have her turn off VoiceOver.
Turning on VoiceOver
You can also turn VoiceOver on and off using the menu, but when it is on it takes more clicks. You can find the feature under Settings > Accessibility > VoiceOver. You can also set the speed of the voice here. I find I have to keep mine closer to the tortoise and the hare so I can follow the text while I am driving. Be aware that touch gestures may be different in this mode. For example, you must click to select, then double click to open items. Scrolling is also different.
Alternatively, I have used Voiceover to read books in the kindle app. I found that I could do one chapter of Hirsch’s Digital Humanities Pedagogy per drive, and I could almost hear Lisa Spiro or Tanya Clement talking as their works were read to me. I also used VoiceOver when riding in an airport shuttle when reading made me queasy.
Using my iPad for this reading means that my iPhone is still free for other uses, like checking traffic on the maps app during traffic jams. I find this type of reading useful for texts I want to familiarize myself with but which I don’t need to go in depth. Since I’ve also saved them to diigo, I can always go back to them when I need to read deeper. VoiceOver works better on connected prose because if you miss a word, you can usually get the meaning by context. Finally, I had to slow the pace of the voice down to make sure I caught everything.
Reflections on a Text Analysis Assignment
In Spring 2013, I taught LAT312K: Intermediate Latin at the University of Texas-Austin. This was the fourth and last required course in the Latin sequence at UT and focused on Vergil’sAeneid.
The course functioned both as a cap to a student’s Latin experience (several of my students were graduating seniors finishing off their required courses) and a gateway into advanced study of Latin literature and culture for Classics majors. One of my goals in the course was introducing students to a variety of approaches scholars take to the study of Latin literature in general and Vergil’s Aeneid in particular. This goal allowed me to include a digital humanities element in the course by having my students experiment with digital methodologies. One such assignment focused on text analysis. I include the assignment below, as well as my reflections on how this pedagogical experiment went.
Assignment Directions
Text Analysis
For most of this semester we have been focusing on a close reading of Latin. Now we’re going to try distant reading. You can find our more about this idea here:
Schulz, Kathryn. “The Mechanic Muse – What Is Distant Reading?” The New York Times, June 24, 2011, sec. Books / Sunday Book Review. http://www.nytimes.com/2011/06/26/books/review/the-mechanic-muse-what-is-distant-reading.html.
For this discussion you are going to play with distant reading Vergil’s Aeneid in English:
1. Read “What is Text Analysis?”: http://tada.mcmaster.ca/Main/WhatTA
2. Play with Text Analysis tools here: http://voyant-tools.org/
a. Find out more about Voyant Tools using the TAPOR Portal (http://www.tapor.ca/) by doing a search for Voyant. Note that some tools have basis descriptions while others have reviews with more information on how to use them. Pick one tool to play with that you think might be useful in analyzing the Aeneid. Please explain why you picked this tool.
b. Find a text of the Aeneid in English.
Try project Gutenberg: http://www.gutenberg.org/browse/authors/v#a129
Be sure to note who the translator is. (see the bibrec tab)
c. Try at least one Voyant tool and compare and contrast the experience of using it to doing a close reading of the text. How useful might this type of analysis be for analyzing the Aeneid? What challenges do you see with this methodology?
Reflections
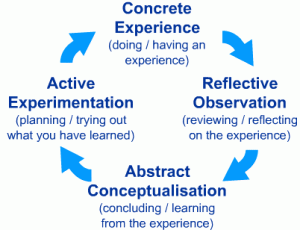
Kolb’s Learning Cycle
This assignment was completed outside of class, with students sharing their results in an online discussion board. Then, we followed our online discussion with an in-class discussion aimed at synthesizing findings and analysis from the online discussion and reflecting on the overall experience. This sequence was designed to follow Kolb’s learning cycle, with students trying out what they had learned about the Aeneid by experimenting with text analysis, leading to a concrete experience, then reflecting on that experience in the online discussion, and using the in-class discussion to draw conclusions from the learning experience. In the in-class discussion I wanted my students to come to the abstract concept of considering how digital tools might change interpretive practice. Linking the online and in class discussions also follows principles of good blended learning design in laying out clear links between in and out of class activities. In class discussion expanded online discussion rather than repeating it. Admittedly, I’m writing my own reflection many months later, but in my opinion I’d say this overall assignment was a partial success. Students were able to complete the assignment–both using the tools and writing the online discussion–but for the most part they did not fall in love with text analysis. Still, our discussion in class did include reflection on issues of digital scholarship and revealed some insights into the text that they gained from the experience.
What Went Wrong or What I Would Change If I Did This Again
I was disappointed that these students didn’t fall in love with digital methodologies. I think I fell prey to the fallacy that I often warn faculty members about–just because it is digital doesn’t mean students will like it. The overall assignment needed better framing to explain why they might use text analysis. I did try to give them some context for distant reading and chose a NY Times article on digital humanities rather than a more specialized digital humanities article because I wanted them to have an accessible text. I think, however, that the article was more negative than I remembered and some students picked up on those negative parts, proclaiming how much they loved close reading and interpretation and how bad distance reading was. (The next week I assigned an article that was a beautiful example of close reading and interpretation–some students criticized that reading because they felt the author pushed the interpretation too far. Then I realized my students were good humanists trained to critique whatever they read.) If I did this assignment again, I would provide the general framing in class and assign only an informational article focused specifically on text analysis as a methodology, e.g., Geoffrey Rockwell’s “What is Text Analysis?” While the debate on the limitations of distant reading is a good one for students to consider, it was also somewhat of a distraction when they hadn’t even tried any sort of computer-assisted text analysis.
I also framed this assignment very much as an experiment and let their own inclinations guide their choice of tool. I wanted them to use the TAPOR portal so they would learn about it as a resource for the future. I also wanted to introduce an element of play into the class. Some of the students chose tools that were less successful than others, so for future assignments I might instead suggest that they choose from a pre-determined set of tools. If this were a different class, I might also include this exercise in a sequence of assignments to scaffold engagement with computer-assisted text analysis.
I think my discussion prompt also unintentionally invites criticism more than a discussion of value. In asking, “How useful might this type of analysis be . . .” and “What challenges . . . ” I set myself up for some negative answers. Based on my past teaching experience, I know that students of the Classics can be very conservative when it comes to technology–after all the discipline of Classics does privilege old things. From the point of view of the Ancient Greeks and Romans, even the codex is a new-fangled invention, not to mention the digital text. While resources like the Perseus Project demonstrate the early engagement of Classics in humanities computing, in the undergraduate curriculum this project is often represented as a resource for texts (a tool for consumption) more than as a tool for analysis (a tool for “generative scholarship” to use Ed Ayers’ term). In other words, undergraduate students of classics can be even more disinclined to think in terms of digital methodologies for scholarship. Though my students mostly brought digital devices to class–laptops, tablets, smart phones–and used them to read our Latin text and take notes, they had not had much practice in using such tools for humanities research (which was, after all, the point of my assignment). Overall, then, I would say I needed to provide more positive framing for this assignment–I misjudged how much I needed to “sell” digital scholarship to my students. In the future I might also start from the tools for analysis built into the Perseus Project, with which they were already familiar rather than Voyant Tools. I had chosen Voyant because of the potential application outside of Classics, but a tool built for Classicists might have been an easier sell.
What Went Right
Despite my dissatisfaction with the results, I do think this assignment was valuable for a number of reasons. First of all, it exposed my students to a methodology of digital scholarship that they might otherwise never have tried. At least one student said that he liked it because it made more sense to him than close reading and interpretation. This reaction demonstrates how quantitative approaches to the humanities can be a bridge to students trained in more quantitative disciplines like the sciences.
The most valuable tools for my students seemed to have been Voyant Cirrus andVoyant Links. Both of these confirmed themes that we had already discussed for the Aeneid. Still, that experience validates the tools rather than offering the new insights I wanted students to gain.
A more interesting insight came from an unexpected place. I was having students analyze translations of the Aeneid (an admittedly flawed approach–in a perfect world they would be analyzing the Latin texts), so some of these insights were based more on the translator than the work of Vergil. I intentionally did not explain how to use stop words (common words like “the”, “and”, “of”, etc., that should be excluded from analysis) because I wanted to see if my students would figure out on their own that this is one challenge of doing text analysis. Some of them did and used the the tool directions to discover how to exclude those words. Other students didn’t use stop words and had some interesting grammatical insights. Because prepositions hadn’t been excluded they noticed how prevalent the words “to”, “for”, “from”, and “by” are in translations of theAeneid. As it happens, these prepositions can be used to translate the dative or ablatives cases from Latin. While I had been drilling them on datives and ablatives for much of the semester, this exercise really drove home to them how important it was that they memorize the various uses of these grammatical cases. Perhaps this insight also just confirms something they should have known already, but it gave them empirical evidence–they didn’t have to just take my word for it. For this insight alone it might be worth it for students to do some text analysis of the Aeneid at the beginning of the semester rather than later. They might also compare multiple translations of the Aeneid by using text analysis without having to read all of them–a truly distant reading–to get an initial look at what themes might emerge.
Learning Outcomes
I would definitely do such an assignment again if I were teaching the same class. With some of the changes I suggested above, I hope it would be more successful. And, whether my students love digital scholarship or not, I still think it is important to expose them to these new methodologies. Even if they do not become professional digital humanists, as Stéfan Sinclair and Geoffrey Rockwell have argued,
From search engine indexing to sophisticated methods of literary analysis, the computer has become an indispensable tool in dealing with the massive influx of digitized textual data in our information age. Liberal arts students need to understand automated methods of text analysis because they underlie how we find, use, and share information today.
Finally, for humanists and scientists alike computer-assisted text analysis affords a different way to look at a text one that might yield insights not easily realized by traditional methods of close-reading.
More Resources and Sample Assignments for Text Analysis
I’ve covered text analysis in many workshops introducing digital humanities. Here are some other resources, sample assignments, and ideas for using text analysis.
Stéfan Sinclair and Geoffrey Rockwell. “Teaching Computer-Assisted Text Analysis: Approaches to Learning New Methodologies.” Digital Humanities Pedagogy: Practices, Principles and Politics, ed. Brett Hirsch. Open Book Publishers, 2013, pp. 241-254.
Sample Assignments
- Distant Reading Duffy by Brian Croxall,http://www.briancroxall.net/dh/assignments/distant-reading-duffy/
- Student example: http://www.briancroxall.net/dh/2011/12/08/voyant-links-analysis/
- Close Reading with Many Eyes (University of Texas):http://www.cwrl.utexas.edu/content/close-reading-manyeyes
- Using Wordle in the classroom:http://chronicle.com/blogs/profhacker/using-wordle-in-the-classroom-1-of-2/22830 (Includes links to visualization resources)
Wordle: http://www.wordle.net/
Wordle is a toy for generating “word clouds” from text that you provide. The clouds give greater prominence to words that appear more frequently in the source text. You can tweak your clouds with different fonts, layouts, and color schemes. The images you create with Wordle are yours to use however you like. You can print them out, or save them to the Wordle gallery to share with your friends.
- Wordles, or the gateway drug to textual analysis:http://chronicle.com/blogs/profhacker/wordles-or-the-gateway-drug-to-textual-analysis/22781
- But also consider this useful critique: “Every time I see a word cloud presented as insight, I die a little inside.” –Jacob Harris. “Word Clouds Considered Harmful.” Nieman Journalism Lab, October 13, 2011.http://www.niemanlab.org/2011/10/word-clouds-considered-harmful/.
Ideas for using Wordle
- Use wordle on an assignment text to pull out key issues and themes. (by student in writing class)
- Use wordle on a paper to make sure the right themes are emphasized. (by writing instructor)
- Use wordle on text survey results to find hidden themes.
Digital Reading Practices for the Liberal Arts Classroom
Today I’m leading a Tech Snack at. St. Edward’s University on “Digital Reading Practices for the Liberal Arts Classroom.” Tech Snacks bring together faculty members, instructional technology staff, and others at St. Edward’s University to discuss the pedagogical uses of various technologies. This tech snack will look at ways that reading has changed in the digital age. My title is borrowed from a NITLE Seminar I organized last year in which Stéfan Sinclair and Geoffrey Rockwell introduced the NITLE community to computer-assisted text analysis via Voyant Tools. When I first proposed this topic, I imagined that I would discuss how I had tried an assignment built around this methodology for the intermediate Latin class on Vergil’s Aeneid that I taught last Spring. I still plan on sharing this example as a way of exploring how computers can offer a different way into the close reading that we typically teach in the literature classroom. That is, computer-assisted text analysis is one of the new methodologies championed by the digital humanities community. But, I also want to spend some time discussing how we might continue traditional reading practices in a digital environment. How do we translate our analog, print reading practices into a digital world and what other affordances might that environment offer?
Earlier this year at our tech snack on mobile devices we ended up focusing on the challenges of reading digitally and replicating print reading practices like highlighting and annotation. One key challenge for students is that there is not a magic bullet in terms of platforms for reading nor even an agreed upon standard to allow for interoperability. I use a variety of tools depending on medium and type of reading (I also documented my reading practices in this earlier post: How Humanists Read and Why We Need a Better (Electronic) Reading Ecosystem):
- Diigo (http://www.diigo.com) for highlighting and annotating the web and saving bookmarks in the cloud with added tags, so I can find them later on any device.
- iAnnotatePDF (http://www.branchfire.com/iannotate/): For reading, highlighting, and taking notes on my iPad.
- Kindle for reading on my iPad and iPhone (I don’t usually use highlights).
- Zotero for tracking bibliography in the cloud with added tags, so I can find entries later on any device. I sometimes export notes from iAnnotate and add them to these records.
- Evernote (http://evernote.com/) for notes from meetings in the cloud with added tags, so I can find them later on any device. I can also clip articles (with annotation) from the web, add tags, and same them to notebooks, but I’m not ready to replace diigo with evernote. I can also forward emails to a notebook with tags. Since much of my work is done via email and meetings, this platform comes closest to aggregating all I need.
- Instapaper (http://www.instapaper.com/) for saving online articles to read later, but I have a bad habit of never getting time to read these.
Most of my reading is done individually and requires ways for me to find things (articles, notes, etc.) later when I need it for some project, talk, workshop, etc. I hope that today’s discussion will get at some of the reading practices we are trying to inculcate in students. What should our learning goals be for student reading practices? I’ll share results from today’s tech snack.
Social Annotation
I also hope we spend some time discussing social annotation because 44% of St. Edward’s faculty who responded to this fall’s survey on Academic Innovation reported that they do not use social annotation but would like to. (Of course, this was also one of the technologies that faculty members also reported they were least familiar with.) The ability to read and annotate collaboratively in real time is one of the affordances offered by a digital medium.
Here are some tools I know about for social annotation:
- Diigo (http://www.diigo.com), especially diigo groups. For one of my favorite examples, see this blog post: “Bringing Web 2.0 to the Classroom“
- Comment Press and Other Collaborative Writing Tools for Word Press: See this run down from Jack Dougherty at Trinity College: http://cowriting.trincoll.edu/
- Hypothes.is (http://hypothes.is/): Haven’t tried this one but I heard about it last month at THATCamp Leadership.
- Classroom Salon (http://www.classroomsalon.com/): Produce heat maps of annotated passages and tag your annotations.
Faculty Mobile Device Mixer
On September 20th Instructional Technology welcomed thirteen faculty, Center for Teaching Excellence staff and Library staff to our first Tech Snack for fall — “Mobile Device Mixer”. We started off by using a mobile app Poll Everywhere to ask faculty to name their favorite app. Poll Everywhere allows you to conduct a quick poll using any mobile device, including laptops.

Note Taking
No surprise that Evernote tops the list! Evernote is a great productivity tool. You can sync notes across multiple devices (Windows, Android, iOS). You can sort notes into notebooks and tag them for easy searching. Ann David shared an educational use for Evernote. She uses Evernote for Learning Logs for her Educational Technology class. Students make Evernote notebooks and share so she can see live what students are writing. She can’t edit or make notes on their notebooks but she can give immediate feedback. Students can include audio, images, and videos to record their experience.
File Management and Sharing
Ryan Hoover discussed the ease of using Google Drive across devices to share documents with students. DropBox also has an app that lets you access files across devices.
Annotation and Reading
We had a lively discussion on tools to annotate PDFs or ebooks via mobile devices. Annotation of PDFs and ebooks is still challenging for some students. Julie Sievers shared her favorite, iAnnotate, which is available for iPads and Android devices.
Other apps we discussed:
- Quip – a shared word processor so everyone is editing the same document. You can add photos to create a collective photo album.
- TalkBoard – a shared whiteboard, great for creative projects
- SimpleNote – a note application available on iOS and Androids
- vBookZ PDF Reader — Reads PDFs to you — great for commuting in Austin!