Elements of Art:
1.) Line: quality (thick, thin, broken), implied line, actual line, linear networks: cross-contours, psychic line.
Example 1: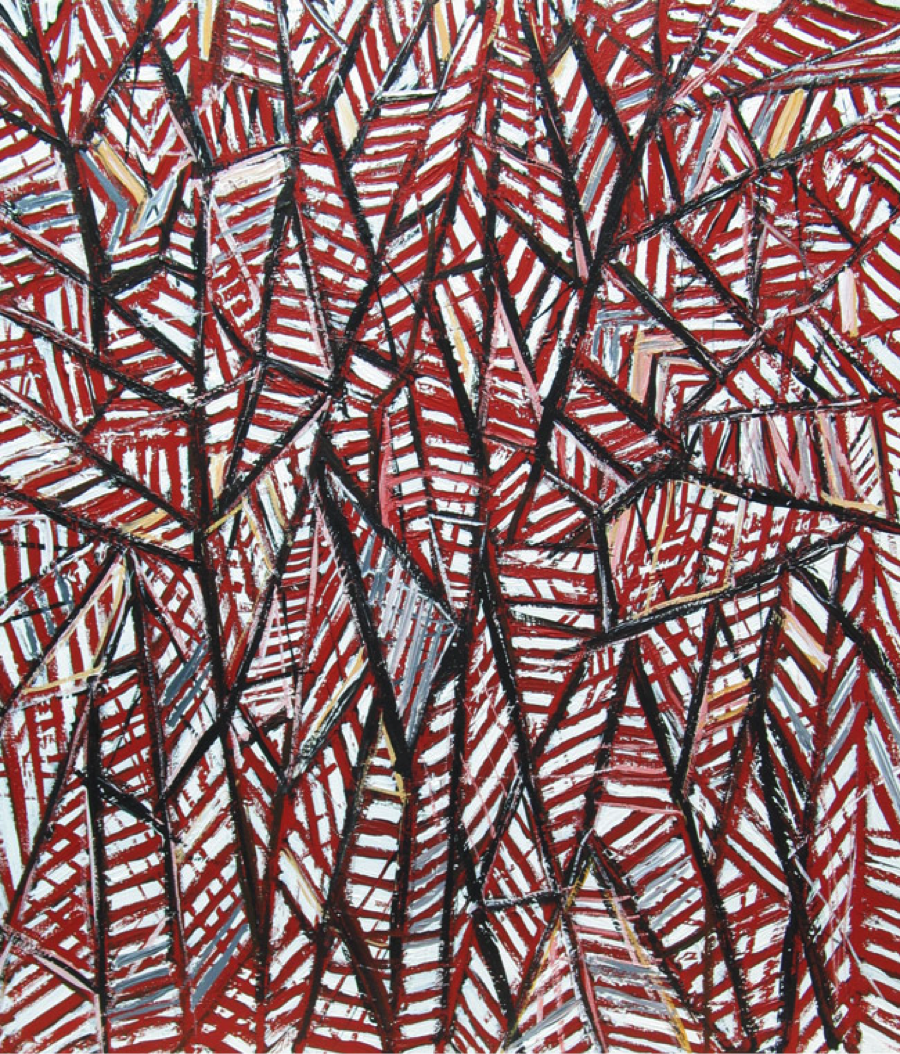 
Example 2: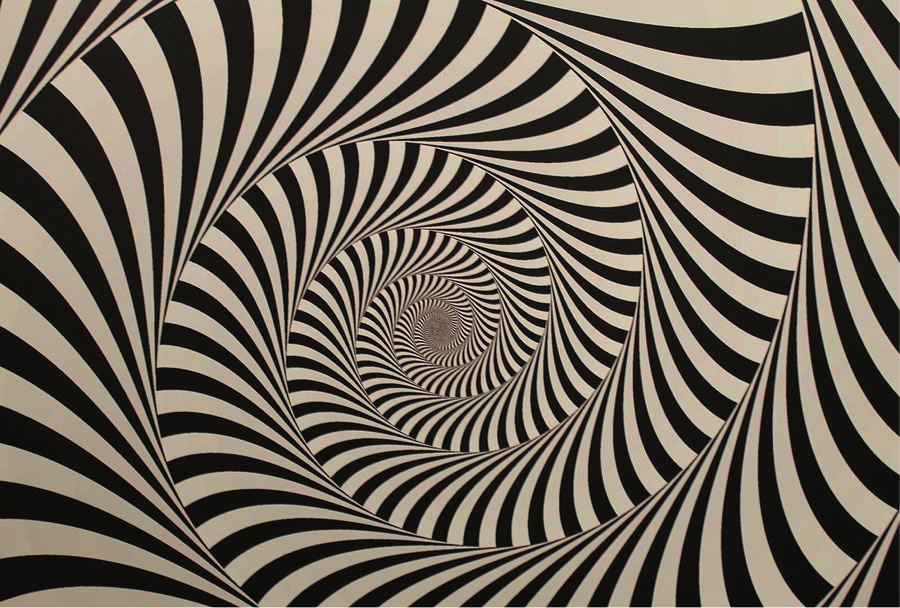 
Example 3: 
Student: Summer Mecham
2.) Shape: is a flattened enclosed area. The boundary of a shape can be created by enclosing an area with a continuous line or implied line, filling an area with solid color/ texture, broken color texture
Example 1: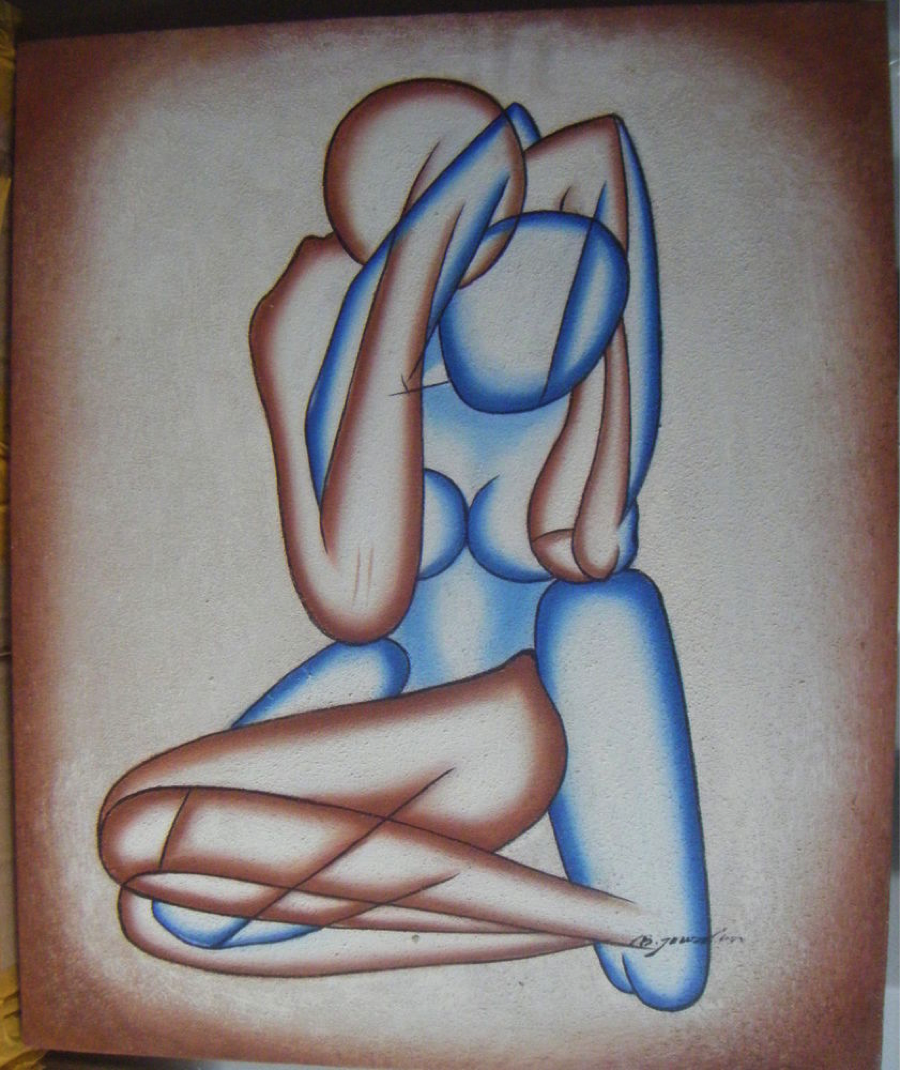 
Example 2: 
Example 3: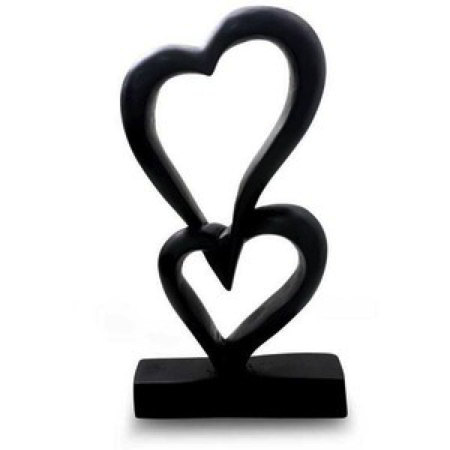 
Student: Summer Mecham
3.) Texture: physical, visual (illusion), invented texture
Example 1: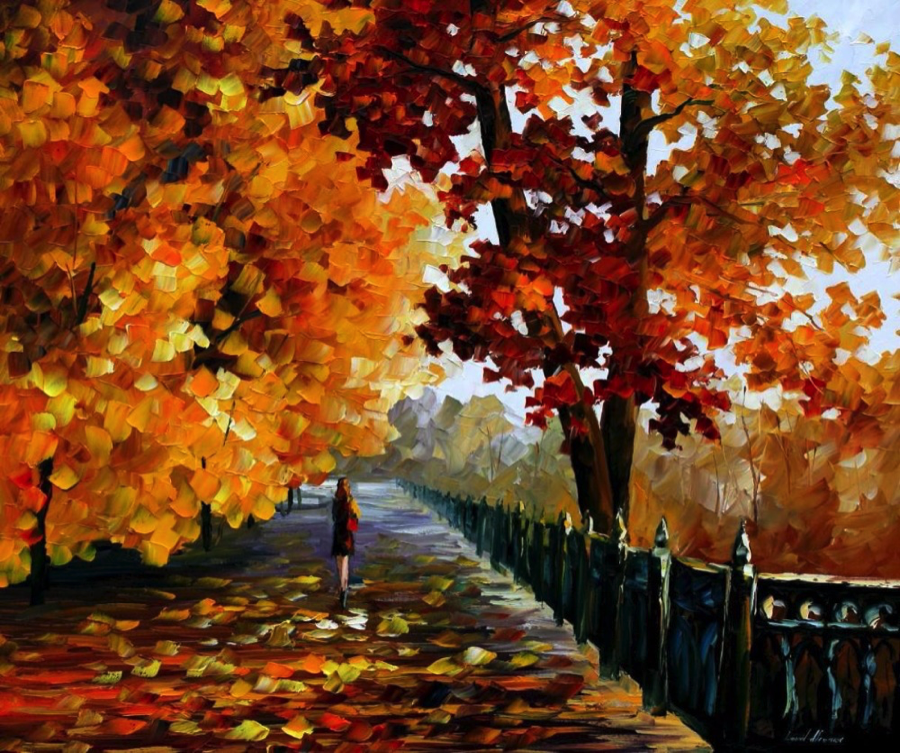 
Example 2: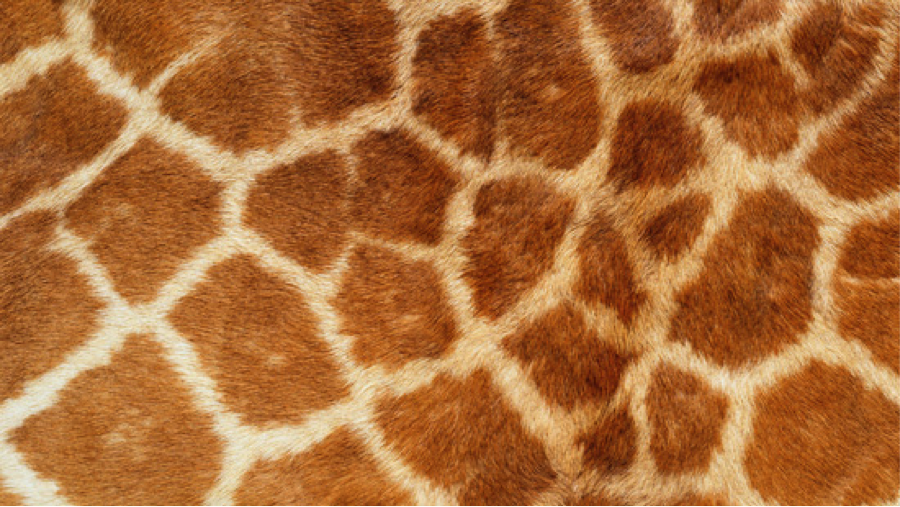 
Example 3: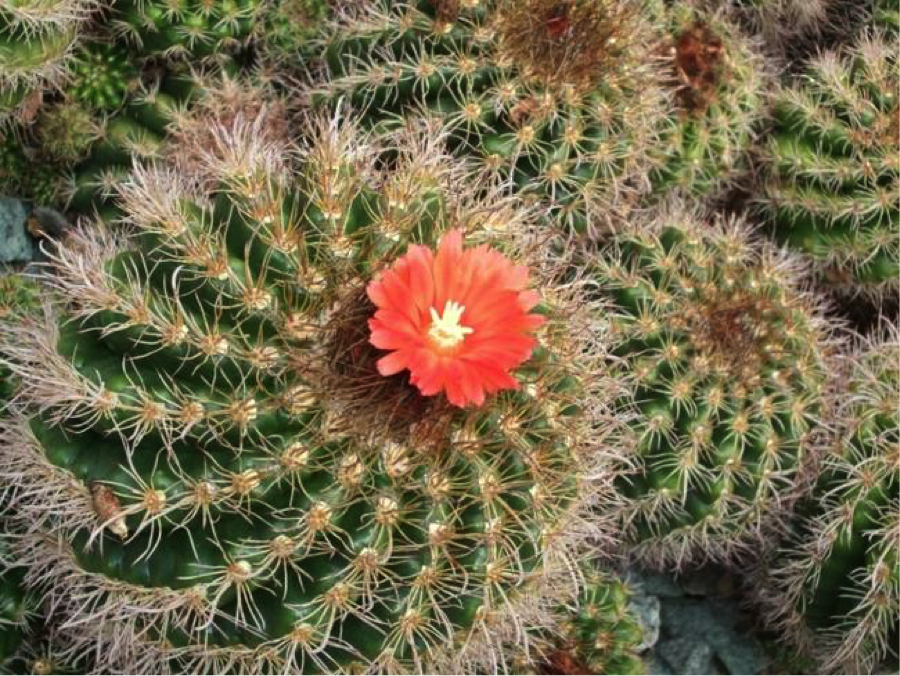 
Student: Summer Mecham
4.) Value: Contrast, value distribution (proportion of lights and darks).
Example 1: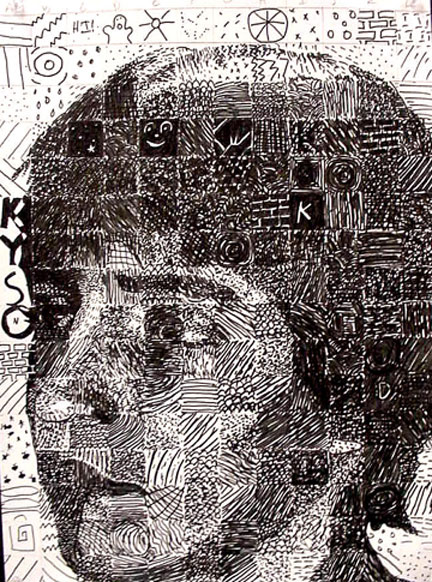 
Example 2: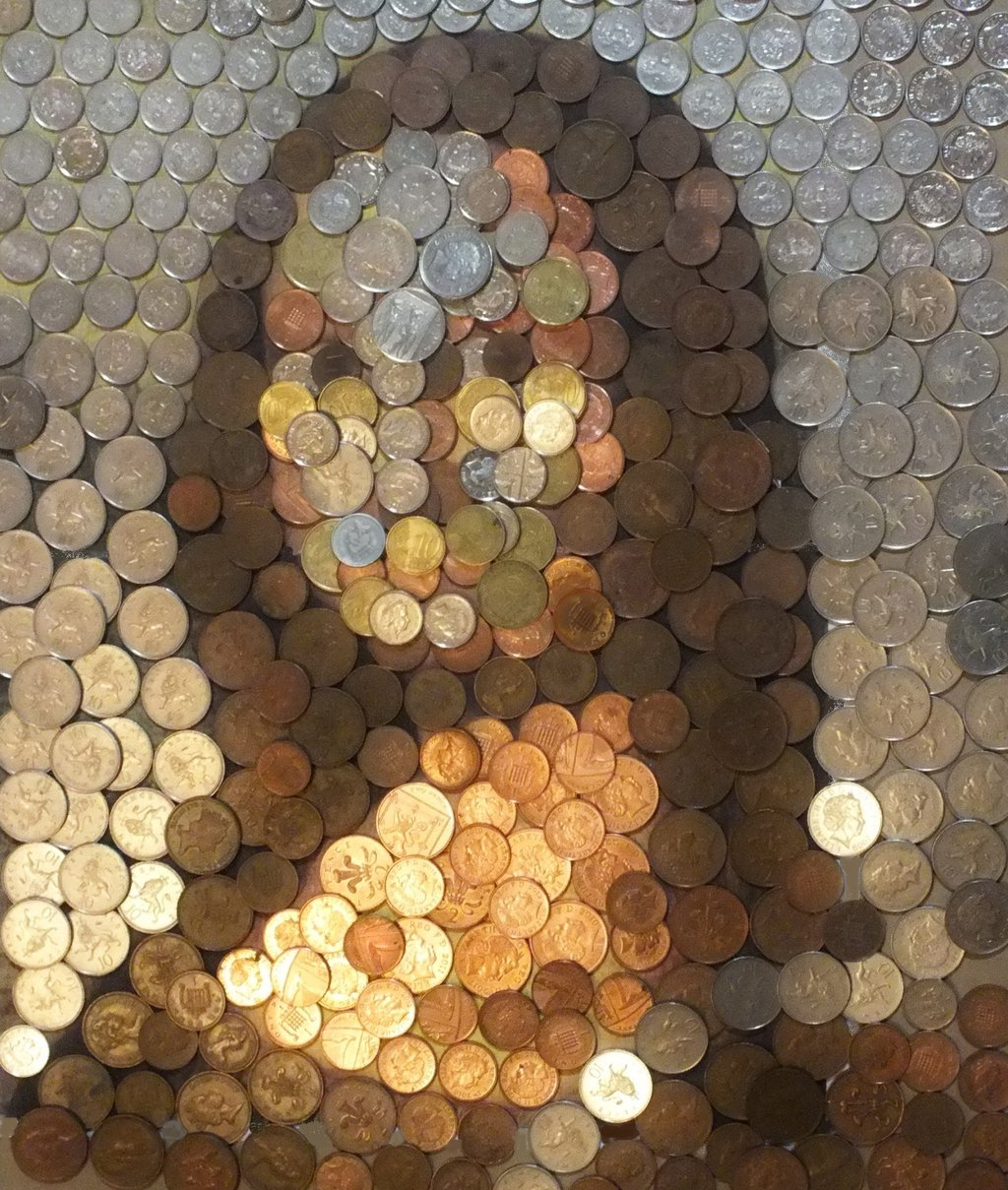 
Example 3: 
Student: Abdullah Alsaif
5.) Color: Color has: HUE< SATURATION< VALUE plus WHITE = TINT plus GRAY = TONE plus BLACK = SHADE
Student: Abdullah Alsaif
6.) Plane: 3-d form that has length and width but with minimal thickness.
Example 1: 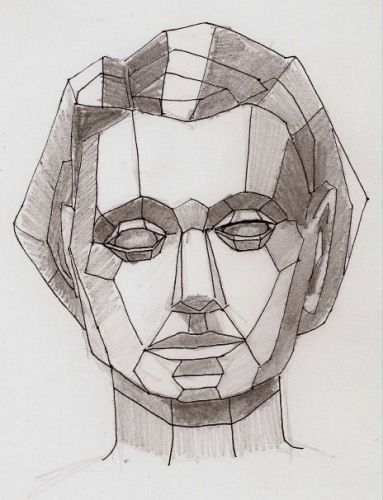
Example 2: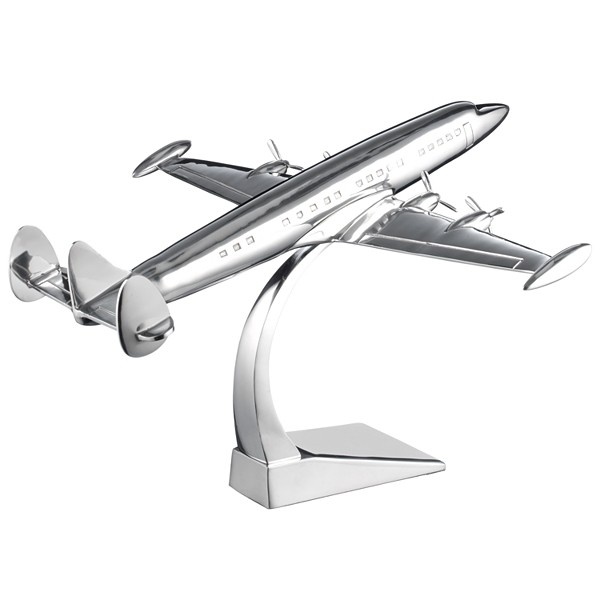 
Example 3: 
Student: Abdullah Alsaif
7.) Volume: refers to enclosed area of 3-d space
Example 1: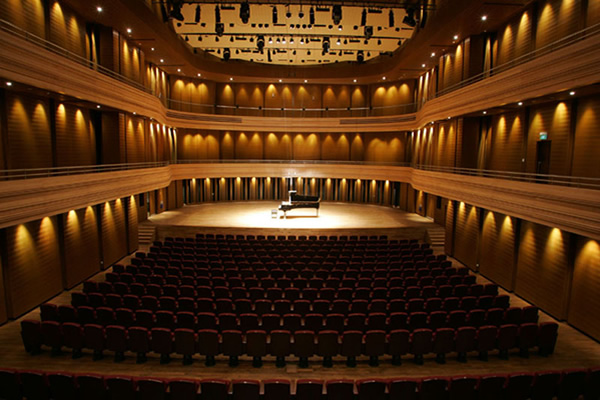 
Example 2: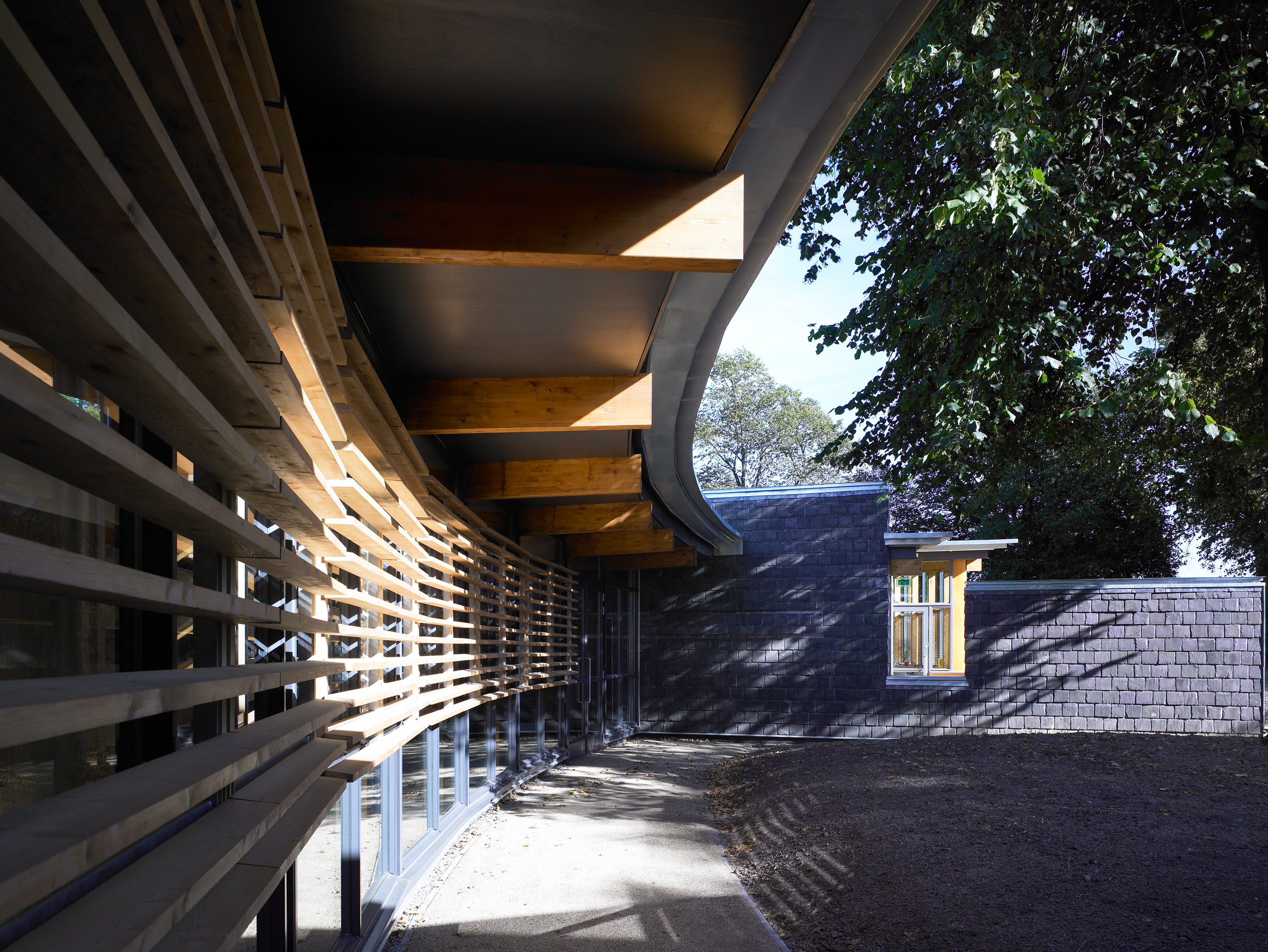 
Example 3: 
Student: Luna
8.) Mass: solid 3-d form
Example 1: 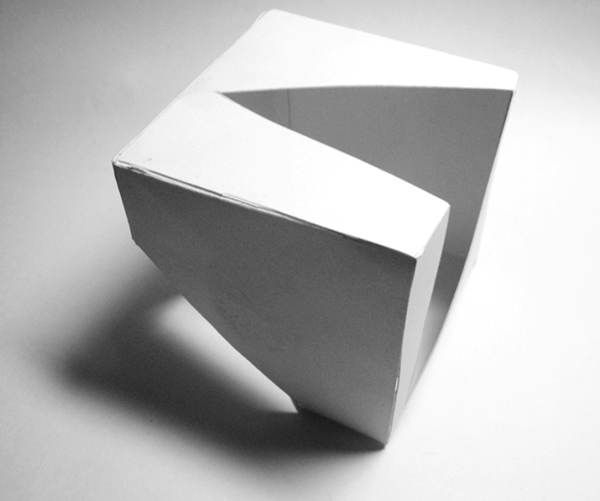
Example 2: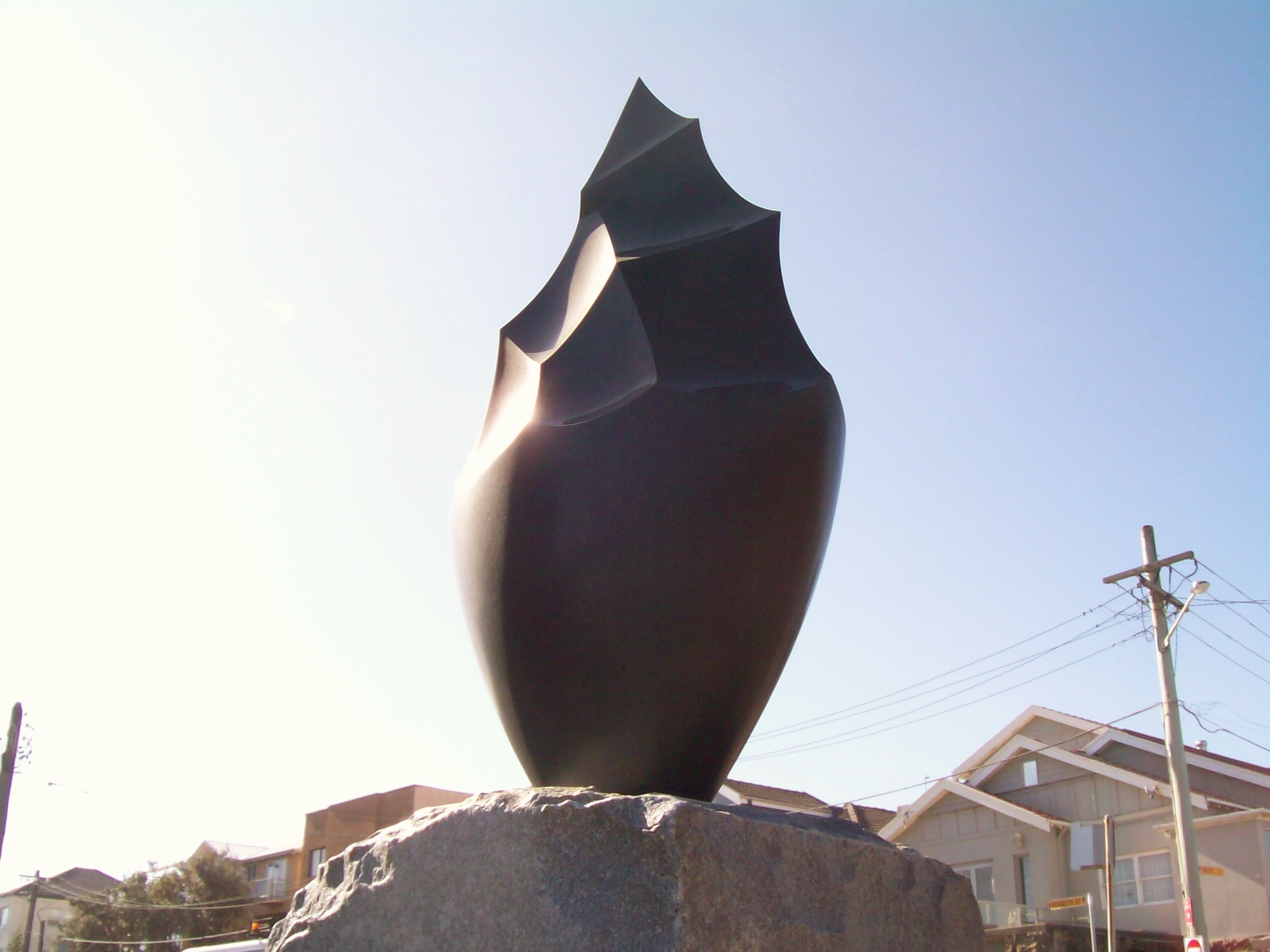 
Example 3: 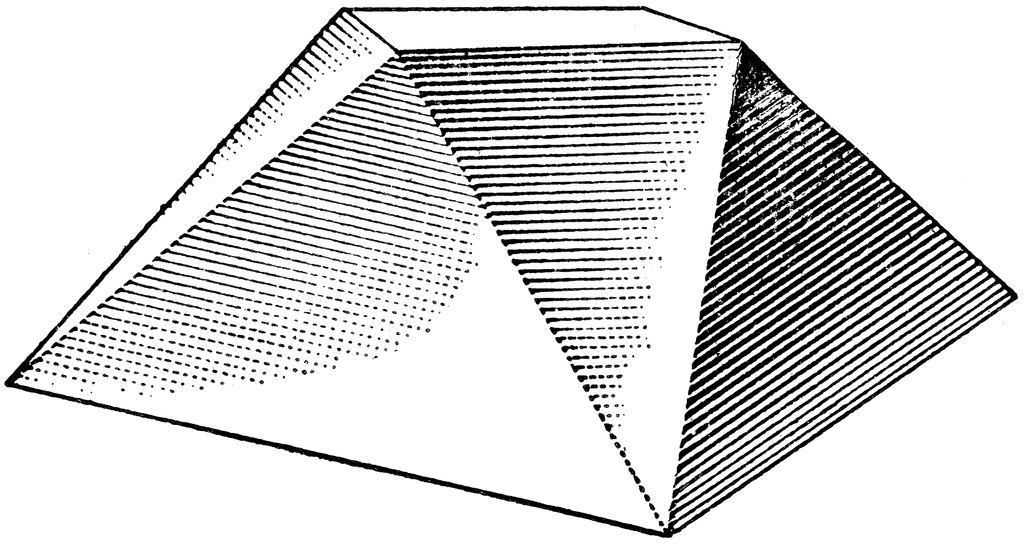
Student: Luna
9.) Space: area within or around an area of substance: positive/negative, compression/expansion, activated, entering.
Example 1: 
Example 2: 
Example 3: 
Student: Luna
10.) Light: can enhance or obscure, affect emotions, entice us to enter, create mystery, can even be the sculptural medium
Example 1: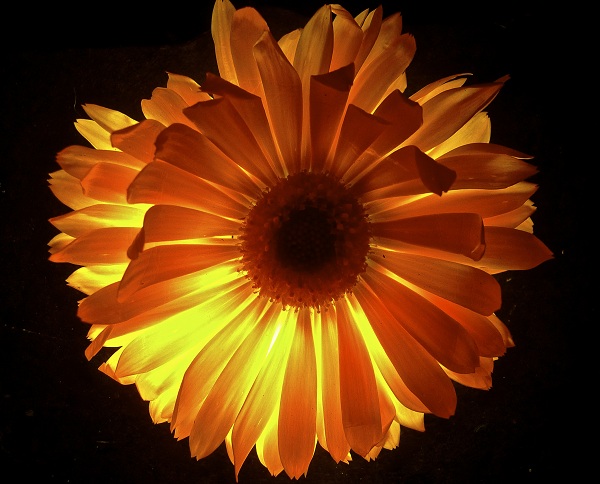 
Example 2: 
Example 3: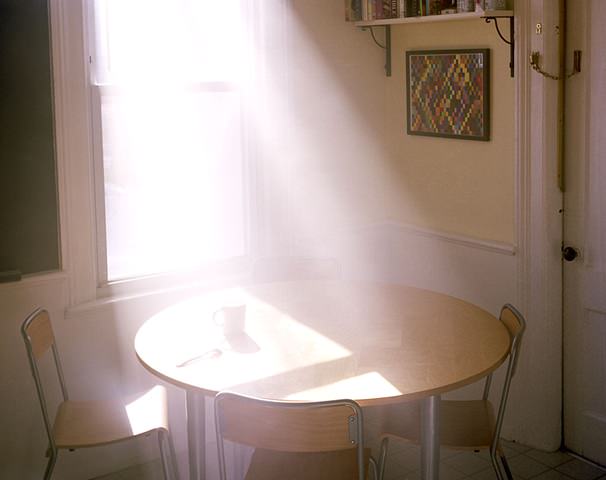 
Student: Tristan Procell
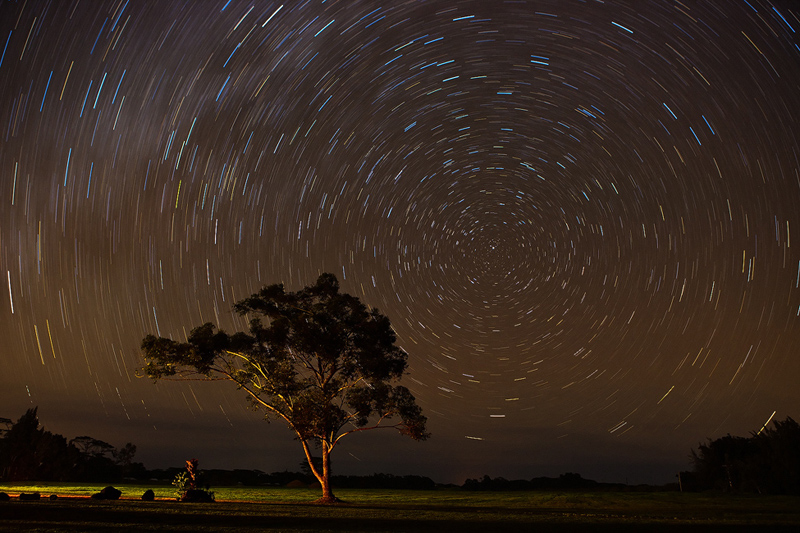
11.) Time/motion: actual and implied are two aspects of time.
Example 1: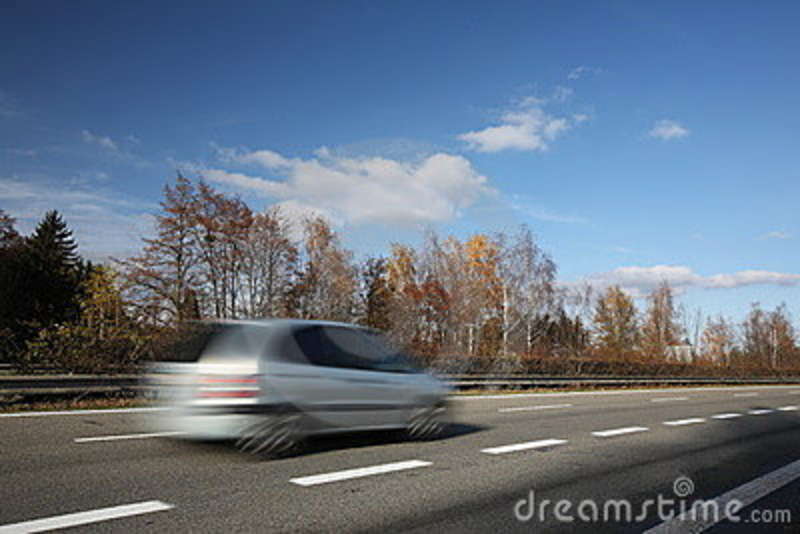 
Example 2: 
Example 3: 
Student: Tristan Procell
Principles of Design
1.) Unity/variety: similarity, oneness, togetherness, cohesion
Example 1: 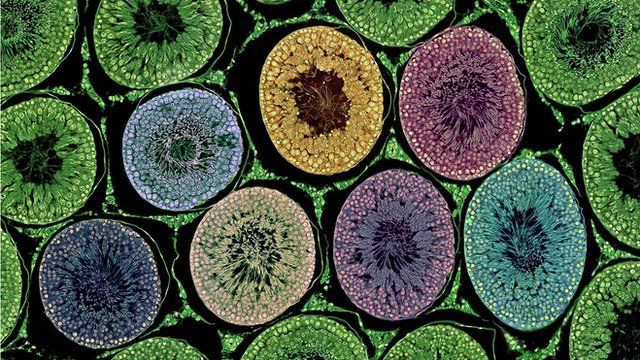
Example 2: 
Example 3: 
Student: Tristan Procell
2.) Balance:
Symmetry/approximate symmetry: visual or actual equilibrium of two halves of a composition mirroring each other in size/shape and placement of elements of art.
Asymmetry: creates equilibrium among visual elements that do not mirror each other on either side of axis. (Depending, design can be quite dynamic or chaotic
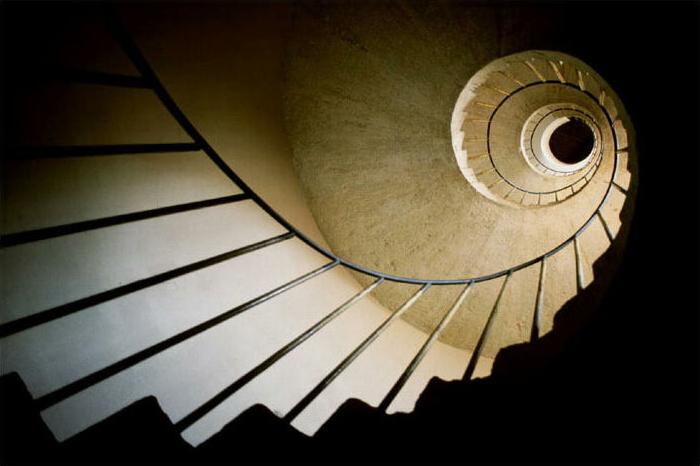
Radial symmetry: equilibrium achieved by elements emanating from a point, usually the center of a composition
Student: Steven Valero
3.) Scale: Comparative size of an element of art or object in relation to other objects and expectations about what is normal. (Ex: human scale)
Proportion: Relationship of the size of parts to each other and to the whole artifact or image
Example 1: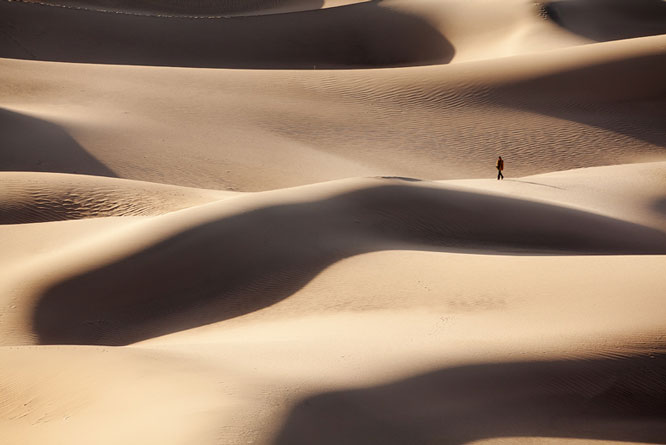 
Example 2: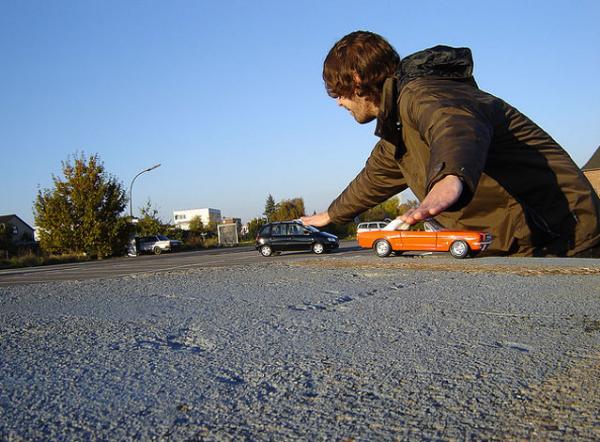 
Example 3: 
Student: Steven Valero
4.) Rhythm: Sense of movement – regular, irregular, pattern, or grid
Example 1:
Student: Steven Valero
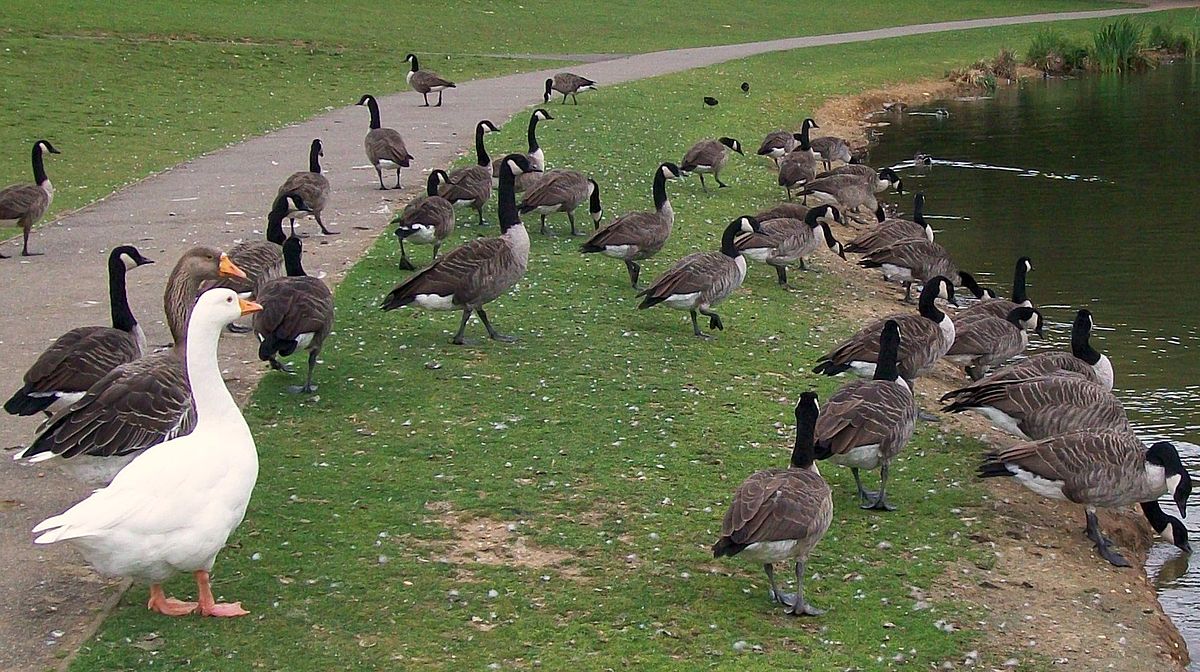
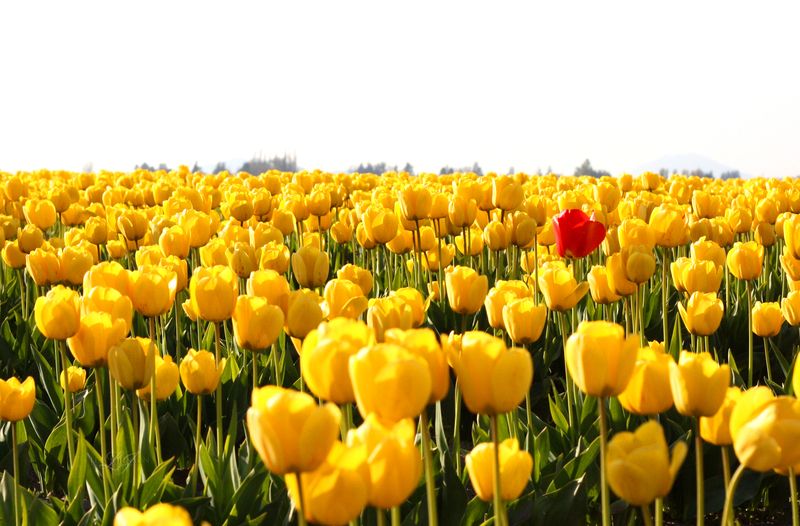
5.) Emphasis: Arrangements of elements of art to make some areas the primary focus of a viewers’ attention
Example 1:
Student: Steven Valero











Recent Comments